Alcohol, a ubiquitous and socially accepted substance, can lead to severe harm when abused. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), alcohol misuse is responsible for more than 200 disease and injury conditions. From brain damage to cancer, excessive drinking can have catastrophic consequences. In this blog, we’ll explore the profound effects of alcohol abuse and offer guidance on recognizing and addressing problem drinking to safeguard your health and the well-being of those around you.
World Health Organization (WHO) – Alcohol and Health
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)

Understanding How Alcohol Impacts the Body:
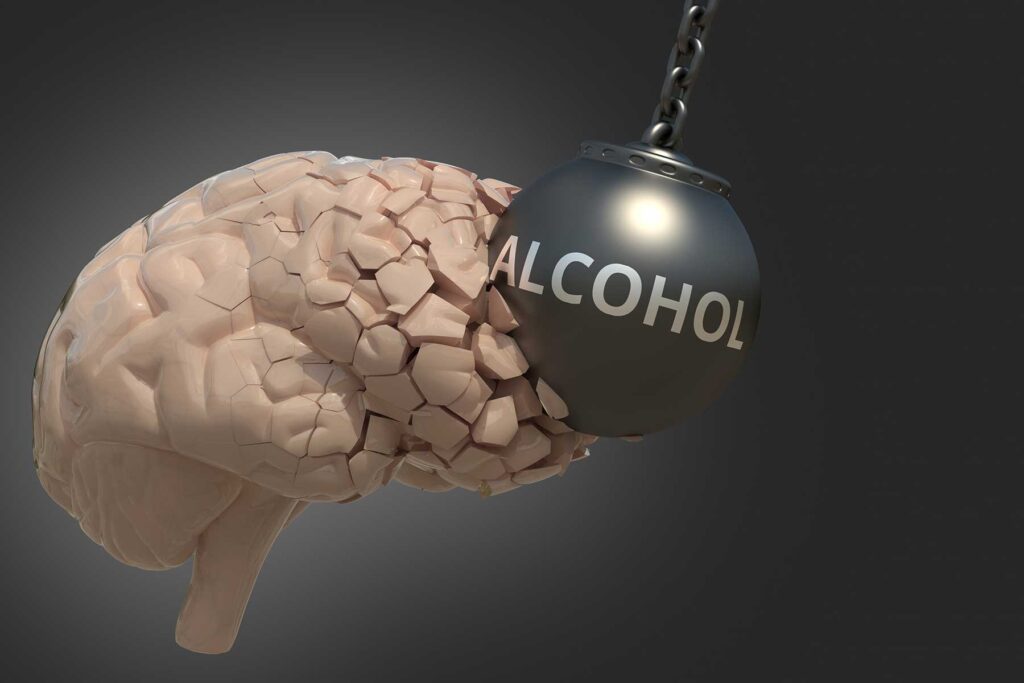
The Brain and Alcohol: Alcohol acts as a central nervous system depressant, causing a slowdown in vital functions, leading to symptoms like slurred speech, blurred vision, and impaired memory. However, it can also exert long-term physical and psychological effects on the body.
Brain Damage: Alcohol interferes with communication pathways in the brain, resulting in cognitive problems and an increased risk of conditions like stroke, dementia, and mental health disorders, sometimes even causing permanent brain damage.
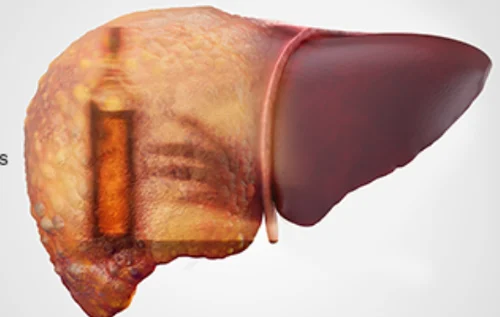
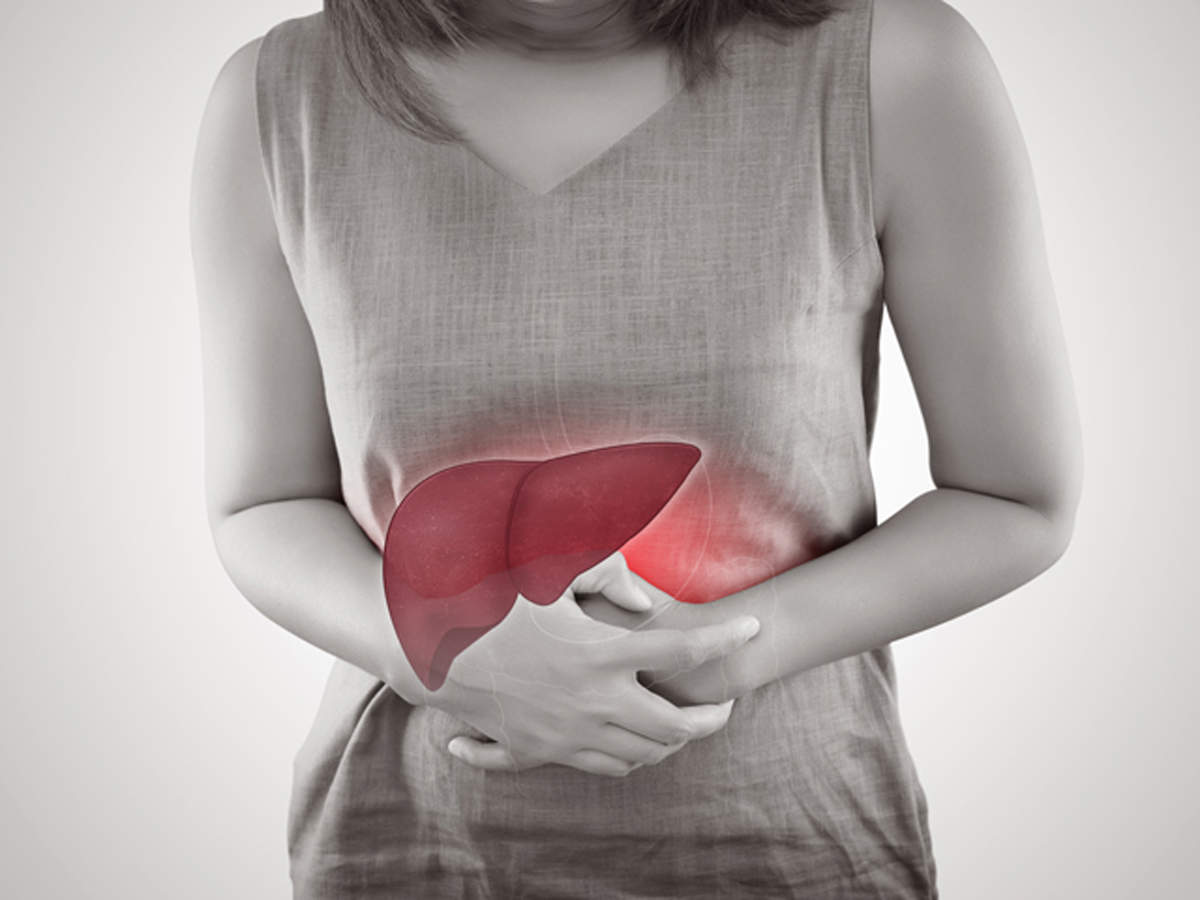
The Liver and Alcohol: The liver is most vulnerable to alcohol’s effects as it metabolizes and eliminates alcohol from the body. Excessive alcohol consumption can overwhelm the liver, leading to various health issues:
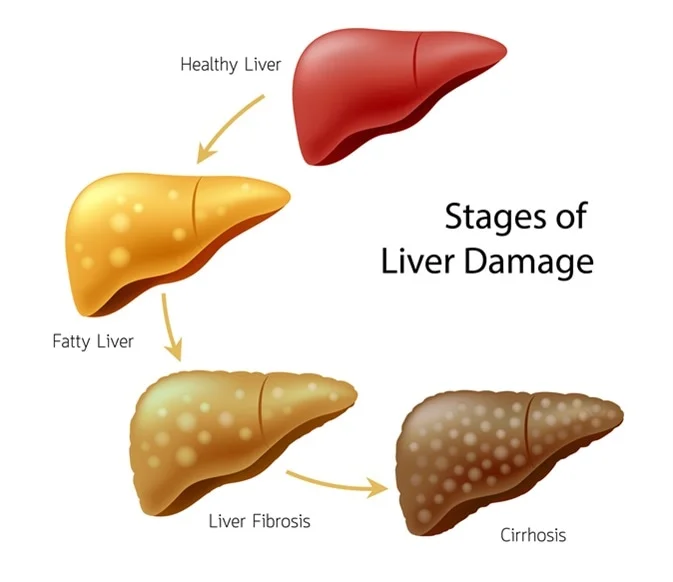
- Liver Damage: Prolonged alcohol abuse causes conditions like fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
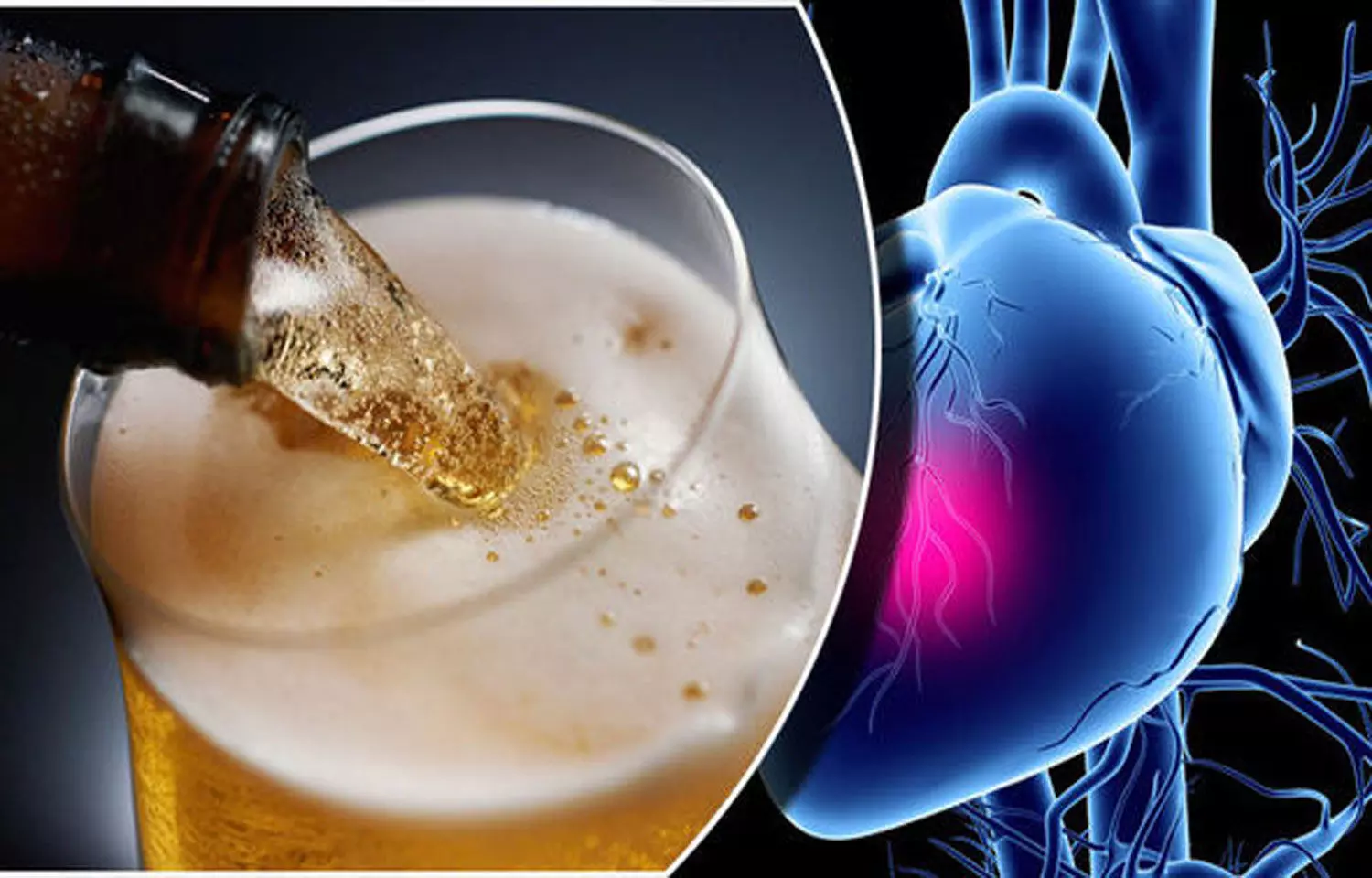
The Heart and Alcohol: Heavy drinking can elevate the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and stroke. Additionally, alcohol can increase blood fat levels (triglycerides) and decrease insulin sensitivity, potentially contributing to diabetes.
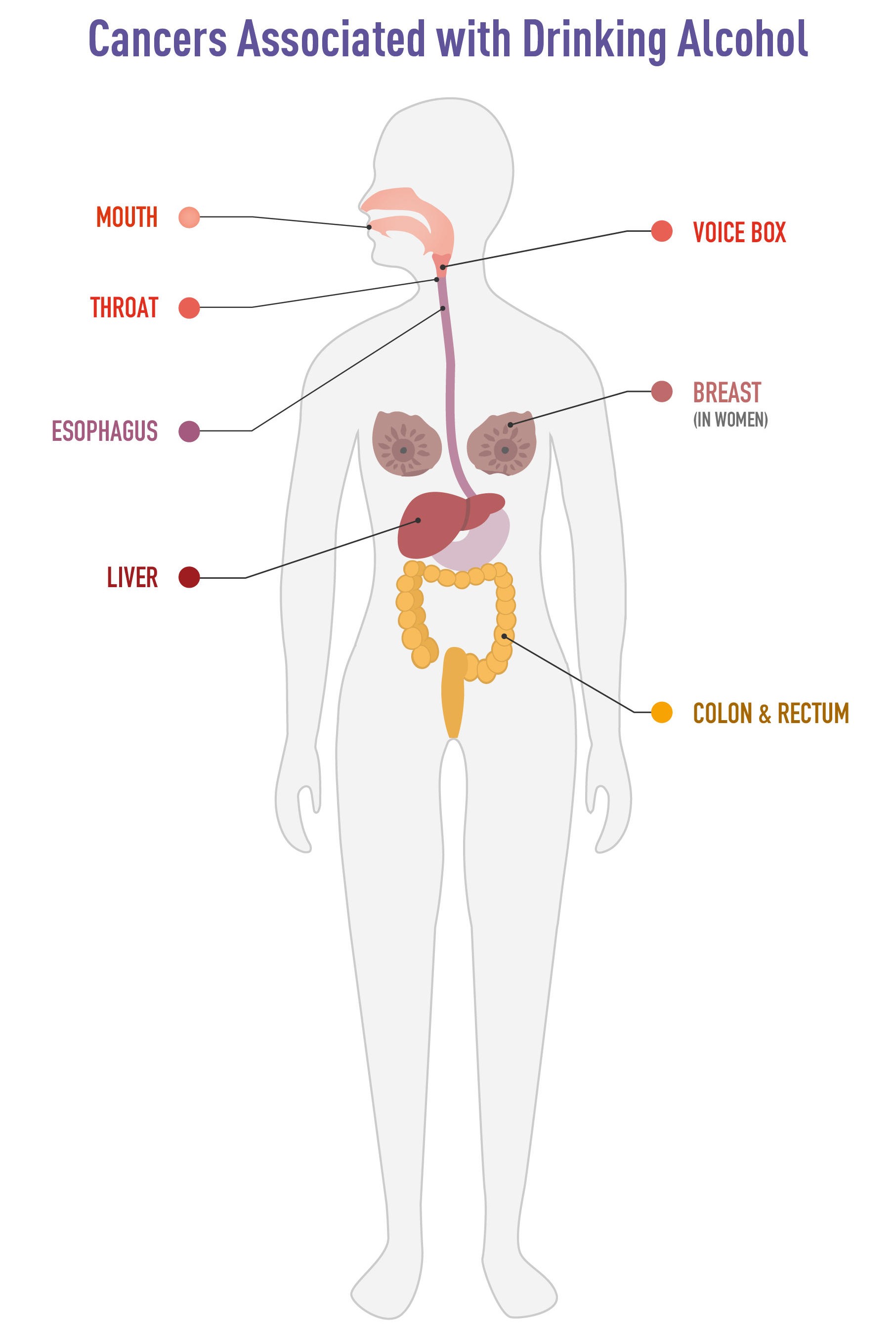
Alcohol and Cancer: Chronic alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, including those affecting the mouth, throat, liver, colon, and breasts.
American Heart Association – Alcohol and Heart Health
Problem drinking can manifest in various ways. Identifying the warning signs is crucial:
- Craving Alcohol for Relaxation: Feeling the need to drink to relax or alleviate stress.
- Excessive Drinking: Consuming more alcohol or drinking for longer durations than intended.
- Loss of Control: Difficulty in controlling drinking habits.
- Neglecting Responsibilities: Neglecting personal, work, or school responsibilities due to alcohol.
- Physical or Psychological Issues: Experiencing health problems and mental health issues resulting from alcohol consumption.
- Legal Troubles: Facing legal consequences due to drinking-related actions.
- Increased Tolerance: Needing more alcohol to achieve the same effect.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Experiencing symptoms like shaking, sweating, or nausea when not drinking.


Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
Addressing Alcohol Abuse:
If you or someone you know is grappling with alcohol abuse, seeking help is crucial. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the problem:
- Therapy: Therapy and counseling sessions can help individuals address the underlying causes of alcohol abuse.
- Medication: In some cases, medications are prescribed to manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous can provide valuable peer support.
- Reducing Access: Limit access to alcohol by removing it from the home and avoiding environments where drinking is predominant.


Alcoholics Anonymous (AA)
Alcohol abuse poses severe and lasting threats to the body, ranging from brain damage to cancer. Recognizing signs of problem drinking and taking proactive steps to limit alcohol access is crucial for addressing this issue. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol abuse, don’t hesitate to seek help. With the right support, recovery and a return to a healthy lifestyle are possible.