Liver cirrhosis is a serious condition, caused by long-term damage to the liver. It occurs when healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, making it impossible for the liver to perform its normal functions. Liver cirrhosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive alcohol consumption, autoimmune diseases, and viral infections such as hepatitis B.
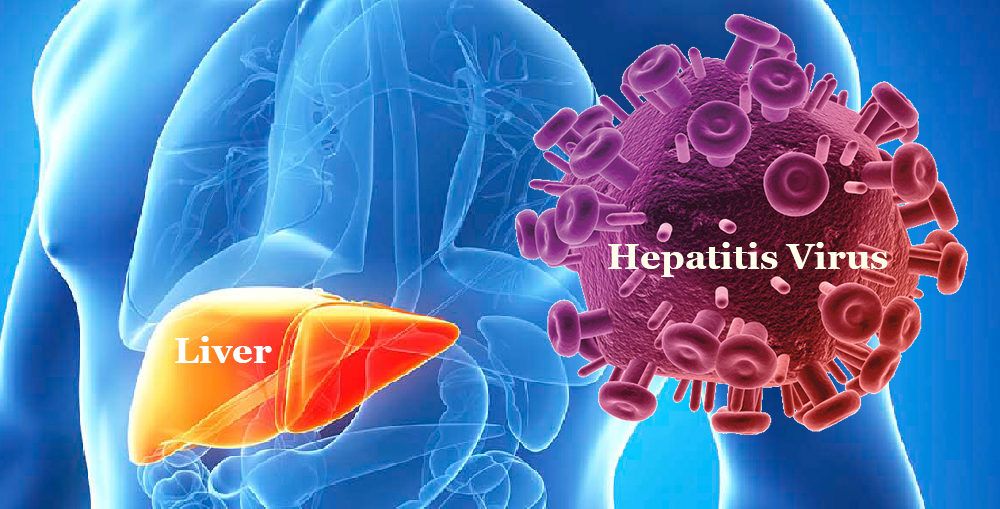
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a virus that infects the liver and can cause inflammation. It is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Approximately 350 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis B, and it is a leading cause of chronic liver disease. Symptoms of hepatitis B may include fever, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, jaundice, abdominal pain, and dark urine.
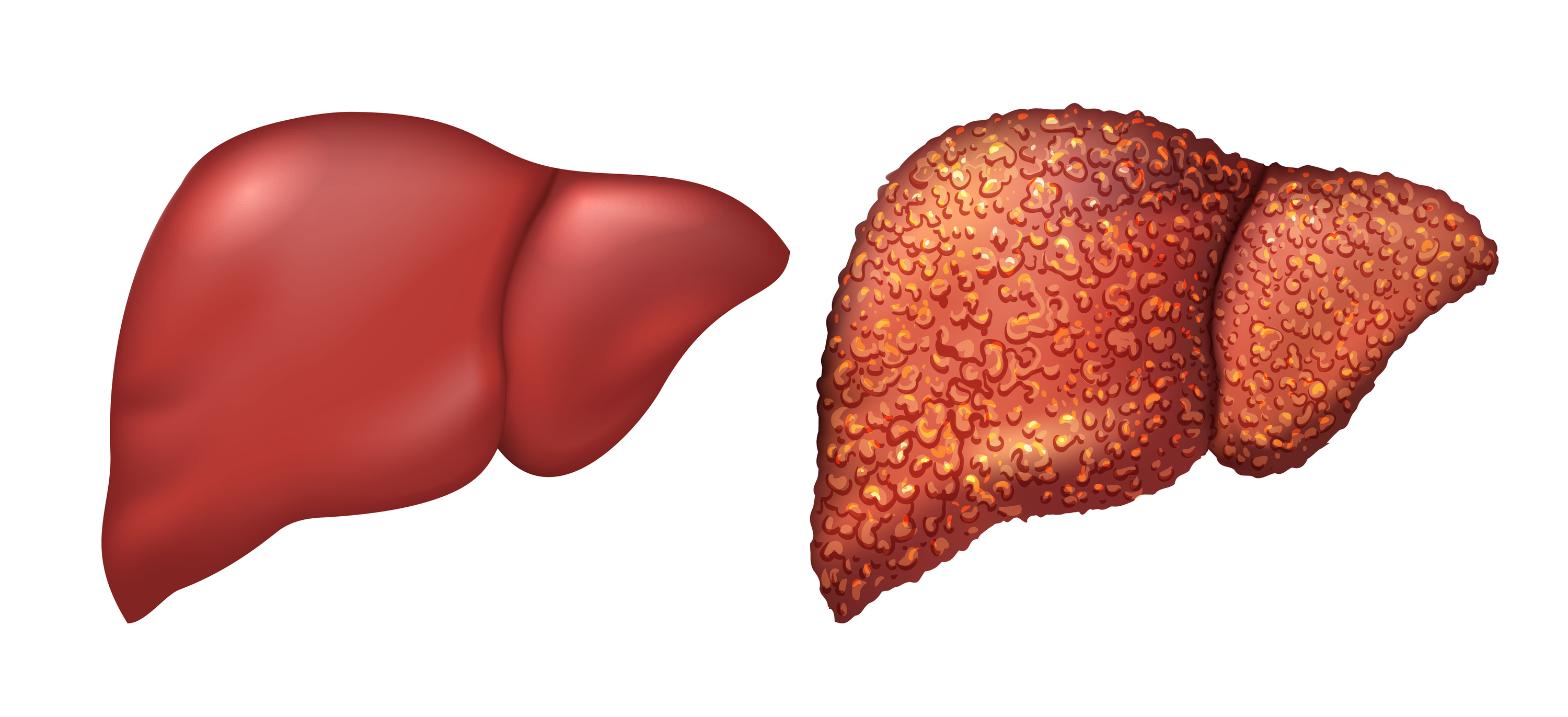
Understanding Liver Cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B
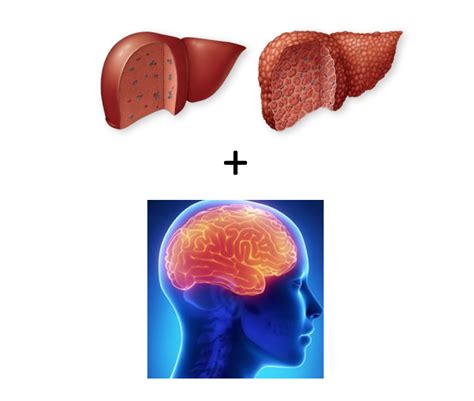
When hepatitis B is left untreated, it can lead to liver cirrhosis. This occurs when healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, blocking the flow of blood and nutrients to the liver. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including a buildup of fluid in the abdomen, fatigue, jaundice, and a condition known as hepatic encephalopathy.
Accumulation of Fluid in Abdomen
One of the most common symptoms of liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis B is the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. This is known as ascites and can cause the abdomen to swell. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which can be caused by an imbalance in proteins and electrolytes. It is important to ensure that the fluid is drained regularly to avoid complications.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a condition that can occur in people with advanced liver cirrhosis. It is caused by a buildup of toxins in the blood, which can affect the brain and cause confusion, drowsiness, memory loss, and even coma. In order to prevent hepatic encephalopathy, it is important to ensure that the liver is functioning properly. This can be done through regular monitoring of liver function tests.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for hepatitis B is antiviral medication. These medications can help to reduce the symptoms of the virus and can even help to reduce the risk of complications such as liver cirrhosis. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary. However, this is a last resort and should only be done when all other treatments have failed.
Prevention
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. The hepatitis B vaccine is very effective and can help to protect against the virus. It is recommended for all adults and children over the age of 11. It is also important to practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia.
Liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis B can be a serious and life-threatening condition. It is important to recognize the symptoms and to seek medical attention immediately if they occur. With proper treatment and management, it is possible to reduce the risk of complications and to improve the overall quality of life.



